Number Systems and Codes
What is a Number System?
A number system is a systematic way of representing numbers using a specific set of symbols or digits. Each number system is characterized by its base (or radix), which determines:
The number of unique digits used
The positional weight of each digit
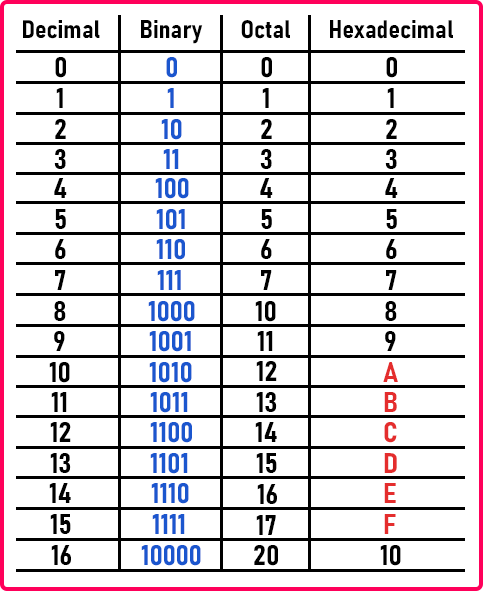
Binary, Octal, Decimal, Hexadecimal conversions :
Binary (base 2): digits 0–1
Octal (base 8): digits 0–7
Decimal (base 10): digits 0–9
Hexadecimal (base 16): digits 0–9 and A–F
A. Decimal to Binary Conversion
Method: Successive Division by 2
Example: Convert 45₁₀ to binary
Division | Quotient | Remainder (LSB → MSB)
45 ÷ 2 | 22 | 1 ← LSB (Least Significant Bit)
22 ÷ 2 | 11 | 0
11 ÷ 2 | 5 | 1
5 ÷ 2 | 2 | 1
2 ÷ 2 | 1 | 0
1 ÷ 2 | 0 | 1 ← MSB (Most Significant Bit)
Result: 45₁₀ = 101101₂
For Fractional Parts: Multiply by 2 method
Example: 0.625₁₀ to binary
0.625 × 2 = 1.25 → 1
0.25 × 2 = 0.50 → 0
0.50 × 2 = 1.00 → 1
Result: 0.625₁₀ = 0.101₂
B. Binary to Decimal Conversion
Method: Positional Multiplication
Example: Convert 110101₂ to decimal
1 1 0 1 0 1
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
2⁵=32 2⁴=16 2³=8 2²=4 2¹=2 2⁰=1
= 32 + 16 + 0 + 4 + 0 + 1
= 53₁₀
C. Decimal to Octal Conversion
Method: Successive Division by 8
Example: Convert 156₁₀ to octal
156 ÷ 8 = 19 remainder 4 ← LSD
19 ÷ 8 = 2 remainder 3
2 ÷ 8 = 0 remainder 2 ← MSD
Result: 156₁₀ = 234₈
D. Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion
Method: Successive Division by 16
Example: Convert 2748₁₀ to hexadecimal
2748 ÷ 16 = 171 remainder 12 (C) ← LSD
171 ÷ 16 = 10 remainder 11 (B)
10 ÷ 16 = 0 remainder 10 (A) ← MSD
Result: 2748₁₀ = ABC₁₆
E. Binary ↔ Octal Conversion
Binary to Octal: Group binary digits in sets of 3 (from right)
Example: Convert 110101101₂ to octal
110 101 101
↓ ↓ ↓
6 5 5
Result: 110101101₂ = 655₈
Octal to Binary: Replace each octal digit with 3 binary bits
Example: Convert 472₈ to binary
4 7 2
↓ ↓ ↓
100 111 010
Result: 472₈ = 100111010₂
F. Binary ↔ Hexadecimal Conversion
Binary to Hex: Group binary digits in sets of 4 (from right)
Example: Convert 10111010111₂ to hexadecimal
0101 1010 1111
↓ ↓ ↓
5 A F
Result: 10111010111₂ = 5AF₁₆
Hex to Binary: Replace each hex digit with 4 binary bits
Example: Convert 3D9₁₆ to binary
3 D 9
↓ ↓ ↓
0011 1101 1001
Result: 3D9₁₆ = 001111011001₂
Quick Reference Table :
1's Complement: To find the 1's complement of a binary number, simply invert each bit (change 0s to 1s and 1s to 0s).
Example: 1's complement of 01101010 is 10010101
2's Complement: To find the 2's complement of a binary number, find the 1's complement and then add 1 to the result. Example: 2's complement of 01101010:
1's complement: 10010101
Add 1: 10010101 + 1 = 10010110
